Context #
A company wishing to implement a Business Continuity Plan may wonder about the accessibility of its public applications. Indeed, if an e-commerce site no longer has a publicly accessible website, then the business continuity plan fails to achieve its purpose.
In the context of Nuabee with OTC, we propose a two-phase DNS approach:
- DRP testing phases: we implement a non-disruptive method so that customers are not affected.
- Actual activation: the transition of clients from the affected infrastructure to the restarted infrastructure in the cloud is seamless.
Both methods use the same technology: DNS.
DRP test #
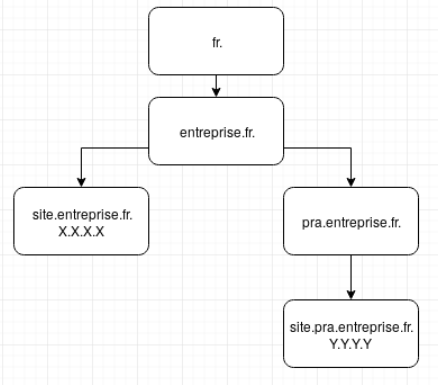
Principle: Subdomain delegation
The DNS protocol supports a feature called zone delegation. In practice, this allows the management of a subdomain to be delegated to a completely different DNS server.
Based on this principle, it is easy for the company to delegate a subdomain such as drp.entreprise.fr to OTC’s DNS servers. The following records must be added to the main DNS zone:
-
drp.company.ge. IN NS ns1.open-telekom-cloud.com. -
drp.entreprise.ge. IN NS ns2.open-telekom-cloud.com.
Nuabee then created a drp.entreprise.fr DNS zone in OTC.
Activation of DRP tests
When activating the DRP in test mode, Nuabee inserts the various records corresponding to the company’s websites into this subdomain, pointing them to the server restarted in the cloud. The resulting DNS tree is as follows:
To test that the recovered website is working properly, simply visit site.drp.company.com in your browser to be redirected to the new server. The original website, still available at site.company.com, is never affected.
Actual activation of the DRP #
When the DRP is actually activated in the event of a disaster, the issue is different. Users must be able to contact services seamlessly. In this case, there are two options.
Option 1: Modification of existing records #
Principle: Update DNS records in the main zone to redirect to the new IP addresses.
Advantages:
- Full control of the DNS zone
- Fine granularity of changes
Disadvantages:
- Time-consuming process for complex areas
- Risk of errors proportional to the number of records
- Extensive manual intervention
Option 2: Full zone delegation (Recommended) #
Principle: Redirecting the entire zone to OTC’s DNS servers by modifying the NS records.
Configuration :
company.de. IN NS ns1.open-telekom-cloud.com.
company.de. IN NS ns2.open-telekom-cloud.com.Advantages:
- Speed of execution: Single modification
- Preservation of the original area: No alteration of the source recordings
- Operational simplicity: Reduced risk of error
Constraints:
- Prior notification to Nuabee for any DNS changes during the activation period
- Temporary dependence on Nuabee teams for DNS changes
Return to normal procedure
Once the DRP is complete, restore the original NS:
company.de. IN NS dns15.tvh.net.
company.de. IN NS ns15.tvh.net.After propagation, DNS resolution resumes normal operation.
Recommandations #
- Opt for full delegation for its speed and reliability
- Anticipating propagation delays in emergency procedures
- Regularly test both mechanisms to validate their effectiveness.
- Document emergency contacts for critical DNS changes